ELECTRICAL FAN CONTROL [SKYACTIV-G 2.0, SKYACTIV-G 2.5]
id0140g2205000
Outline
• Through cooling of the radiator and condenser by operation of the cooling fan according to vehicle conditions, engine reliability and cooling performance have been improved.
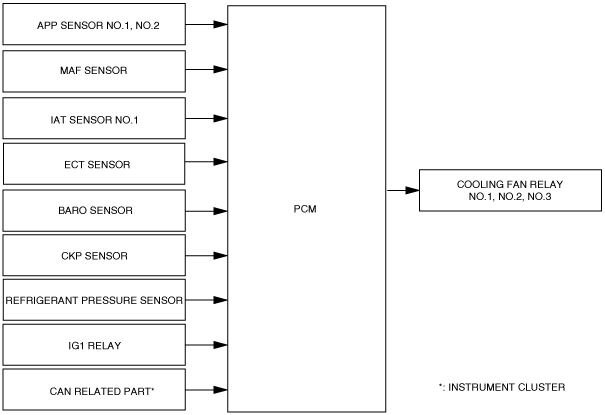
Block Diagram
Operation
• The PCM determines the demand airflow volume by the following conditions.
Operation Pattern
|
Demand airflow volume
|
Cooling fan relay
|
Cooling fan motor
|
|
No.1
|
No.2/No.3
|
No.1
|
No.2
|
|
No airflow
|
OFF
|
OFF
|
Stop
|
Stop
|
|
Small
|
ON
|
OFF
|
Low-speed
|
Low-speed
|
|
Large
|
ON
|
ON
|
High-speed
|
High-speed
|
Engine coolant temperature condition
-
• Controls the PCM output duty ratio according to the engine coolant temperature.
• The control temperature while the engine coolant temperature is decreasing is controlled differently than when it is increasing.
-
• If high-load driving continues with low wind blowing against the vehicle, air bubbles in the fuel line could occur by the rise in the fuel temperature from the heat of the engine. To prevent poor engine starting performance by air trapped in the fuel line from the occurrence of air bubbles, if the following conditions are met, the PCM operates the cooling fan (Demand airflow volume: Low).
• To suppress overheating, the cooling fan is operated when the engine coolant temperature is high. The demand airflow volume is large or small depending on the engine coolant temperature.
A/C operation condition
-
• Controls the demand airflow volume depending on the refrigerant pressure and vehicle speed when the A/C switch is on.
|
Operation condition
|
Demand airflow volume
|
|
• When any of the following conditions is met.
-
― Refrigerant pressure: 1.3 MPa {13 kgf/cm2, 189 psi} or less, vehicle speed: 45 km/h {28 mph} or more
― Refrigerant pressure: 2.2 MPa {22 kgf/cm2, 319 psi} or less, vehicle speed: 85 km/h {53 mph} or more
|
No airflow
|
|
• When any of the following conditions is met.
-
― Refrigerant pressure: 1.3 MPa {13 kgf/cm2, 189 psi} or less, vehicle speed: 45 km/h {28 mph} or less
― Refrigerant pressure: 1.3—1.5 MPa {14—15 kgf/cm2, 189—217 psi}, vehicle speed: 85 km/h {53 mph} or less
― Refrigerant pressure: 1.5—2.2 MPa {16—22 kgf/cm2, 218—319 psi}, vehicle speed: 65—85 km/h {41—52 mph}
|
Small
|
|
• When any of the following conditions is met.
-
― Refrigerant pressure: 1.5—2.2 MPa {16—22 kgf/cm2, 218—319 psi}, vehicle speed: 65 km/h {40 mph} or less
― Refrigerant pressure: 2.2 MPa {22 kgf/cm2, 319 psi} or more
|
Large
|
After Cooling Control
-
• If the engine is stopped directly after driving continuously at high load, air bubbles could occur in the fuel line due to the increase in the fuel temperature by the engine heat. To prevent poor engine starting performance by air trapped in the fuel line from the occurrence of air bubbles, if the following conditions are met, the PCM operates the cooling fan for a maximum period of 9 min (demand airflow volume: Low).
-
― Engine coolant temperature: 90°C {194 °F} or more
― Accumulated heat in engine compartment is extremely high
Conditions during collision
-
• If a collision signal from the SAS control module is received, the PCM stops the engine cooling fan to avoid use of battery voltage.